Understanding Red
Light Therapy
Discover how red and near-infrared light therapy works at the cellular level to reduce pain, accelerate healing, and improve performance.
THE SCIENCE OF RED LIGHT THERAPY
Photobiomodulation uses specific wavelengths of light to trigger biological effects in your cells, promoting healing and recovery.
RED LIGHT THERAPY WAVELENGTH SPECTRUM
Red Light – Optimal for skin regeneration and surface tissue repair
RED LIGHT (630–660NM)
- Skin regeneration
- Collagen production
- Superficial tissue repair
NEAR-INFRARED (810–850NM)
- Deep tissue penetration
- Joint & muscle recovery
- Nerve regeneration
Penetrates 2–3mm into tissue
Penetrates 5–10mm into tissue
Light Output
12–15 J/cm²
Wavelengths
633nm & 850nm
Power Density
80–100 mW/cm²
Treatment Time
60–90 seconds
A Revolution in Healing
Discover why modern LED-based light therapy is a safer, more effective, and practical alternative to traditional lasers for a vast array of conditions.
Enhanced Safety
LEDs produce virtually no heat, eliminating the risk of tissue damage. They emit a diffuse light, making them safe for the eyes without needing protective eyewear.
Wider Treatment Area
The wider aperture of LED probes allows for the treatment of larger body areas like the back and neck, making sessions faster and more efficient.
Practical & Portable
Lightweight, robust, and often battery-operated, LED devices are perfect for both clinical and home use, offering unparalleled convenience.
Cost-Effective
LED technology is significantly more affordable than traditional lasers, making advanced light therapy accessible to more people.
A Versatile Treatment for Numerous Conditions
By enhancing cellular energy and promoting natural healing, Red light is effective across a wide range of applications.
Orthopedic
- Soft Tissue Injuries
- Arthritic Conditions
- Fracture Healing
- Nerve Regeneration
Respiratory
- Sinusitis & Rhinopathy
- Bronchospasm
- Inflammatory Lung Tissue
- Asthma Support
Dermatological
- Acne & Eczema
- Psoriasis
- Keloid Scars
- Cold Sores (Herpes)
Vascular & Wounds
- Acute & Chronic Wounds
- Venous Ulcers
- Lymphatic Drainage
- Pressure Sores
Cellular Response to Light Therapy
How Light Therapy Works
Understanding the science behind photobiomodulation therapy
LIGHT ABSORPTION
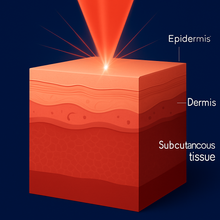
Red and near-infrared wavelengths (630-850 nm) penetrate the skin and are absorbed by cellular photoreceptors.
CELLULAR STIMULATION
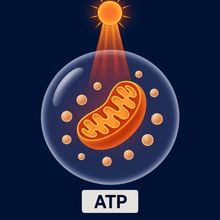
The light energy boosts mitochondrial ATP production, triggering a cascade of beneficial cellular effects.
HEALING RESPONSE

Inflammation drops, circulation rises and tissue repairs faster, delivering natural pain relief.
Key Therapeutic Benefits
REDUCED INFLAMMATION
Decreases inflammatory markers and cytokines, reducing swelling and associated pain.
IMPROVED CIRCULATION
Increases blood flow and formation of new capillaries for better oxygen delivery.
ACCELERATED REPAIR
Stimulates collagen production and cell proliferation for faster tissue and wound healing.
PAIN RELIEF
Reduces nerve sensitivity and increases endorphin production for natural pain relief.
Real results from Photizo light therapy
KNEE OSTEOARTHRITIS
"After years of knee pain and limited mobility, I was skeptical. After just 4 weeks of consistent treatment, I’ve experienced significant pain reduction and can now walk much further without discomfort."
Treatment: 90 seconds, twice daily for 4 weeks
SPORTS INJURY RECOVERY
"As a competitive runner, muscle injuries can derail my training. After a grade 2 calf strain, I was back to light running in 10 days using Photizo—far faster than the expected 3–4 weeks."
Treatment: 60 seconds, 3x daily for 10 days
POST-SURGERY RECOVERY
"My surgeon was amazed at how quickly my incision healed. The physical therapist noted I achieved range-of-motion goals weeks ahead of the typical timeline."
Treatment: 60 seconds, twice daily for 3 weeks
Clinical Outcomes Summary
Research & Evidence
Key scientific studies supporting the efficacy of photobiomodulation therapy for pain, recovery, and cellular health.
Journal of Athletic Training
Therapeutic Photobiomodulation Before Strenuous Exercise Attenuates Shoulder Muscle Fatigue
Lasers in Medical Science
High-Intensity versus Low-Level Laser Therapy in Patients with Knee Osteoarthritis
Journal of Biophotonics
Photobiomodulation in Human Muscle Tissue: An Advantage in Sports Performance?
Key Research Findings
Cellular Effects
- Increases ATP production by 19–30% in treated cells
- Stimulates release of nitric oxide, improving blood flow
- Reduces oxidative stress by neutralizing free radicals
- Activates stem cells and growth factors for tissue repair
Clinical Outcomes
- 57% average reduction in chronic pain intensity
- 41% faster recovery from muscle fatigue and damage
- 63% improvement in wound healing rates
- 76% of patients report improved quality of life
Light Therapy Glossary
Key terms to understand photobiomodulation therapy
Photobiomodulation (PBM)
The scientific term for light therapy that uses red and near-infrared wavelengths to stimulate cellular function, reduce inflammation, and promote healing.
Wavelength
Measured in nanometers (nm), wavelength determines the color of light and its penetration depth. Red light (630-660nm) and near-infrared (810-850nm) are most therapeutic.
Joules
The unit of energy delivered during treatment. Optimal therapeutic dose typically ranges from 3-15 joules per cm² depending on the condition being treated.
Power Density
Measured in mW/cm², this indicates the intensity of light delivered to tissues. Effective therapeutic ranges are typically 30-100 mW/cm².
Chromophores
Light-sensitive molecules in cells that absorb photons. Cytochrome c oxidase in mitochondria is the primary chromophore in red/NIR light therapy.
Mitochondria
The "powerhouse" of cells that produce ATP energy. These organelles are primary targets of red and near-infrared light therapy.
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
The primary energy carrier in cells. Light therapy increases ATP production, providing more energy for cellular repair and regeneration.
Nitric Oxide
A signaling molecule released during light therapy that improves blood flow, oxygen delivery, and triggers various healing mechanisms.
Cytokines
Signaling proteins involved in inflammation. Light therapy helps regulate pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines to promote healing.
Biphasic Dose Response
The principle that light therapy follows a "sweet spot" pattern—too little energy has no effect, while too much can inhibit benefits.
